Imagine standing in the middle of a field, watching as the sky turns an eerie shade of green. Suddenly, a funnel cloud begins to form, twisting and turning like a giant snake in the sky. Tornado formation causes have fascinated scientists and terrified communities for centuries. But what exactly triggers these powerful vortexes? In this article, we'll dive deep into the science behind tornadoes and uncover the factors that contribute to their formation.
Tornadoes are one of nature's most destructive forces, capable of leveling entire towns in mere seconds. Understanding the causes behind tornado formation is crucial for improving early warning systems and saving lives. From supercell thunderstorms to atmospheric instability, we'll explore the key ingredients that come together to create these monstrous twisters.
Whether you're a weather enthusiast, a student of atmospheric science, or simply someone curious about the forces shaping our planet, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of tornado formation causes. Let's get started!
Read also:Dave Franco Age The Journey Of A Hollywood Heartthrob
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Tornado Formation
- The Role of Supercell Thunderstorms
- Wind Shear: The Invisible Force
- Atmospheric Instability
- Moisture and Humidity
- Lifting Mechanisms
- From Funnel Cloud to Touchdown
- Types of Tornadoes
- Predicting Tornadoes
- Tornado Safety Tips
Introduction to Tornado Formation
So, what exactly is a tornado? Simply put, it's a violently rotating column of air that forms between the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud. Tornadoes can vary in size and intensity, with some being relatively weak and others packing winds over 300 mph. But what causes these weather phenomena to form?
Let's break it down. Tornado formation is a complex process that involves multiple atmospheric conditions coming together at just the right time. Think of it like baking a cake – you need all the right ingredients in the right proportions to create something truly spectacular. In the case of tornadoes, those "ingredients" include wind shear, atmospheric instability, moisture, and lifting mechanisms.
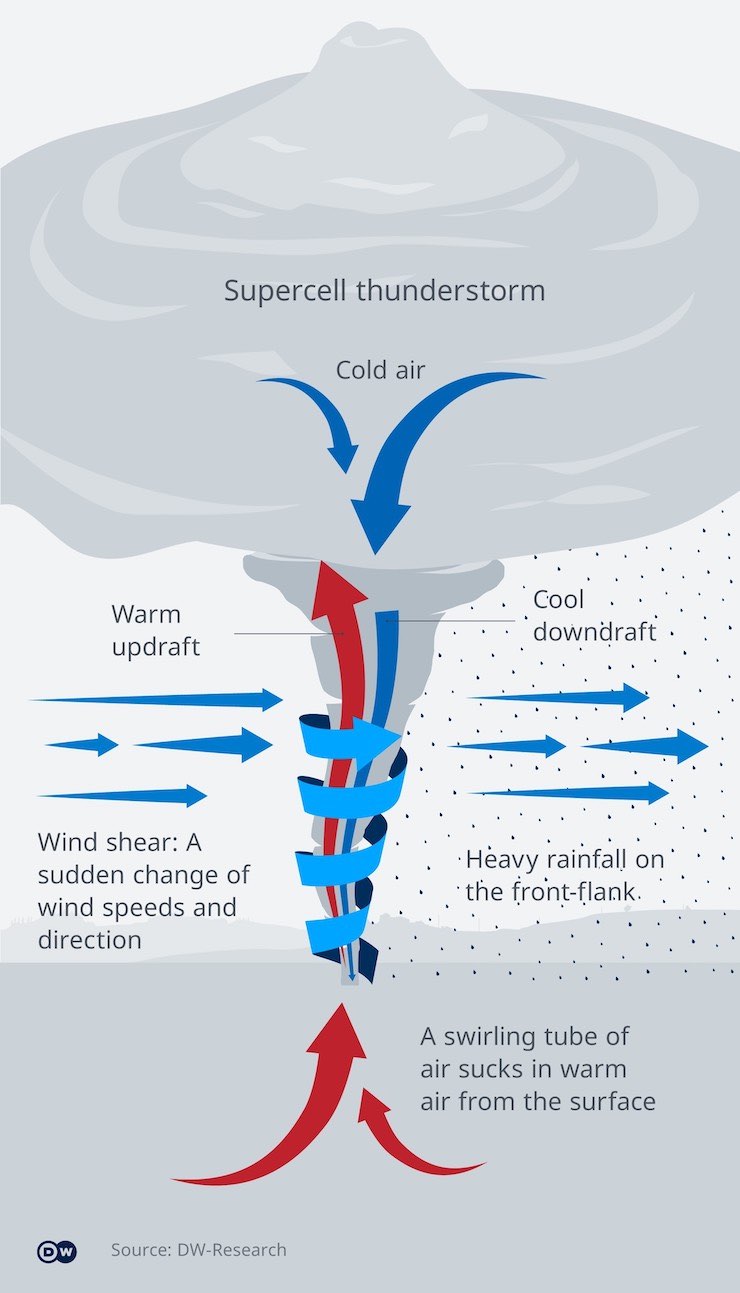
The Role of Supercell Thunderstorms
What is a Supercell?
Supercell thunderstorms are the most likely type of storm to produce tornadoes. Unlike regular thunderstorms, supercells have a rotating updraft called a mesocyclone. This rotation is crucial for tornado formation. But how does a regular thunderstorm turn into a supercell?
- Strong winds at different altitudes create wind shear
- This wind shear tilts the storm's updraft
- The tilted updraft allows the storm to last longer
- The storm's rotation intensifies, creating a mesocyclone
Wind Shear: The Invisible Force
Why is Wind Shear Important?
Wind shear refers to the change in wind speed and direction with height. This invisible force plays a crucial role in tornado formation. Without wind shear, tornadoes simply wouldn't exist. Here's how it works:
Imagine the atmosphere as layers of wind moving at different speeds and directions. When these layers interact, they create areas of rotation. If this rotation is tilted vertically by a strong updraft, it can lead to the development of a tornado. It's like spinning a top – the faster and more consistent the spin, the more likely it is to stay upright.
Read also:Piracy Sites The Dark Side Of The Internet And What You Need To Know
Atmospheric Instability
Atmospheric instability is another key factor in tornado formation. This occurs when warm, moist air near the surface meets cooler, drier air aloft. The warm air rises rapidly, creating the updrafts necessary for tornado formation.
Think of it like a pot of boiling water. When you heat water on a stove, the hot water rises and the cooler water sinks. This creates convection currents that drive the weather system. In the case of tornadoes, these convection currents can become incredibly powerful, leading to the formation of violent storms.
Moisture and Humidity
The Role of Water Vapor
Moisture is essential for tornado formation. Without sufficient water vapor in the atmosphere, thunderstorms simply can't develop the energy needed to produce tornadoes. But where does this moisture come from?
- Gulf of Mexico: A major source of warm, moist air for tornado-prone regions
- Evaporation: Water from lakes, rivers, and oceans adds moisture to the atmosphere
- Transport: Wind patterns carry this moisture into areas prone to severe weather
Lifting Mechanisms
What Triggers the Storm?
Lifting mechanisms are the final piece of the puzzle when it comes to tornado formation. These mechanisms force warm, moist air to rise, initiating the storm process. Some common lifting mechanisms include:
- Fronts: Cold and warm fronts can trigger thunderstorms
- Drylines: Boundaries between dry and moist air masses
- Mountains: Orographic lifting occurs when air is forced over elevated terrain
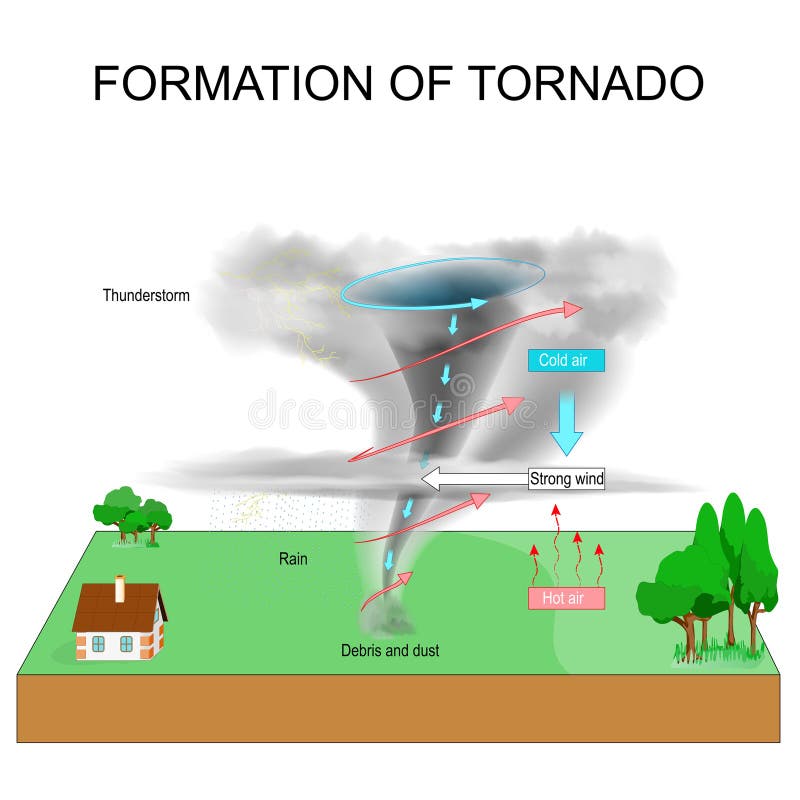
From Funnel Cloud to Touchdown
The Birth of a Tornado
Once all the necessary conditions are in place, a funnel cloud begins to form. This rotating column of air extends downward from the base of the thunderstorm. If it makes contact with the ground, it becomes a tornado. But what happens during this process?
The funnel cloud's rotation intensifies as it descends, creating a vortex of high-speed winds. Debris and dust are often picked up by the tornado, making it visible to the naked eye. This is the moment when the storm reaches its full destructive potential.
Types of Tornadoes
Not All Tornadoes Are the Same
Tornadoes can be classified into several types based on their characteristics:
- Weak tornadoes: EF0 and EF1, with winds up to 110 mph
- Strong tornadoes: EF2 and EF3, with winds up to 165 mph
- Violent tornadoes: EF4 and EF5, with winds exceeding 166 mph
Each type of tornado poses different levels of threat to life and property. Understanding these classifications helps meteorologists issue appropriate warnings and alerts.
Predicting Tornadoes
The Science of Forecasting
Predicting tornadoes is a challenging but essential task for meteorologists. Advances in technology have greatly improved our ability to forecast these storms, saving countless lives in the process. Some of the tools used in tornado prediction include:
- Doppler radar: Detects rotation within thunderstorms
- Computer models: Simulate atmospheric conditions to predict storm development
- Satellite imagery: Provides a bird's-eye view of weather patterns
Tornado Safety Tips
Knowing what to do during a tornado can make all the difference. Here are some essential safety tips:
- Seek shelter in a basement or interior room on the lowest floor
- Stay away from windows and exterior walls
- Protect your head and neck with a helmet or cushion
- Have an emergency kit ready with supplies for at least 72 hours
Remember, tornadoes can strike with little warning, so it's important to stay informed and prepared at all times.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, tornado formation causes are a complex interplay of atmospheric conditions that come together to create these powerful storms. From supercell thunderstorms to wind shear and atmospheric instability, each factor plays a crucial role in the development of tornadoes. By understanding these causes, we can better predict and prepare for these natural disasters.
So, what's the next step? Share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about tornado safety. And if you're interested in learning more about weather phenomena, be sure to check out our other articles on the subject. Stay safe, stay informed, and remember – nature is powerful, but so are we when we work together!