Mathematics can sometimes feel like a foreign language, filled with terms and concepts that might sound intimidating at first. But don’t sweat it, because we’re here to break it down for you in a way that’s super easy to understand. If you’ve ever wondered, “What is the range in math?” you’re in the right place. Whether you’re a student trying to ace your math test or just someone curious about how numbers work, this article will walk you through everything you need to know about the range in math. So, grab a snack, sit back, and let’s dive in!
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let’s set the stage. The range in math is one of those concepts that pops up in various areas of mathematics, from basic arithmetic to advanced statistics. It’s like the unsung hero of number analysis, helping us understand how data is spread out. Understanding this concept opens doors to interpreting data in everyday life, from analyzing test scores to tracking weather patterns.
Here’s the thing about math—it’s not as scary as it seems. Once you get the hang of the basics, everything else starts to fall into place. So, whether you’re here to learn for school, work, or just personal interest, we’ve got your back. Let’s make math less intimidating and more approachable. Ready? Let’s go!
Read also:My Mew Character Unlocking The Secrets Of This Fascinating Feline Persona
Understanding the Basics: What Exactly is the Range in Math?
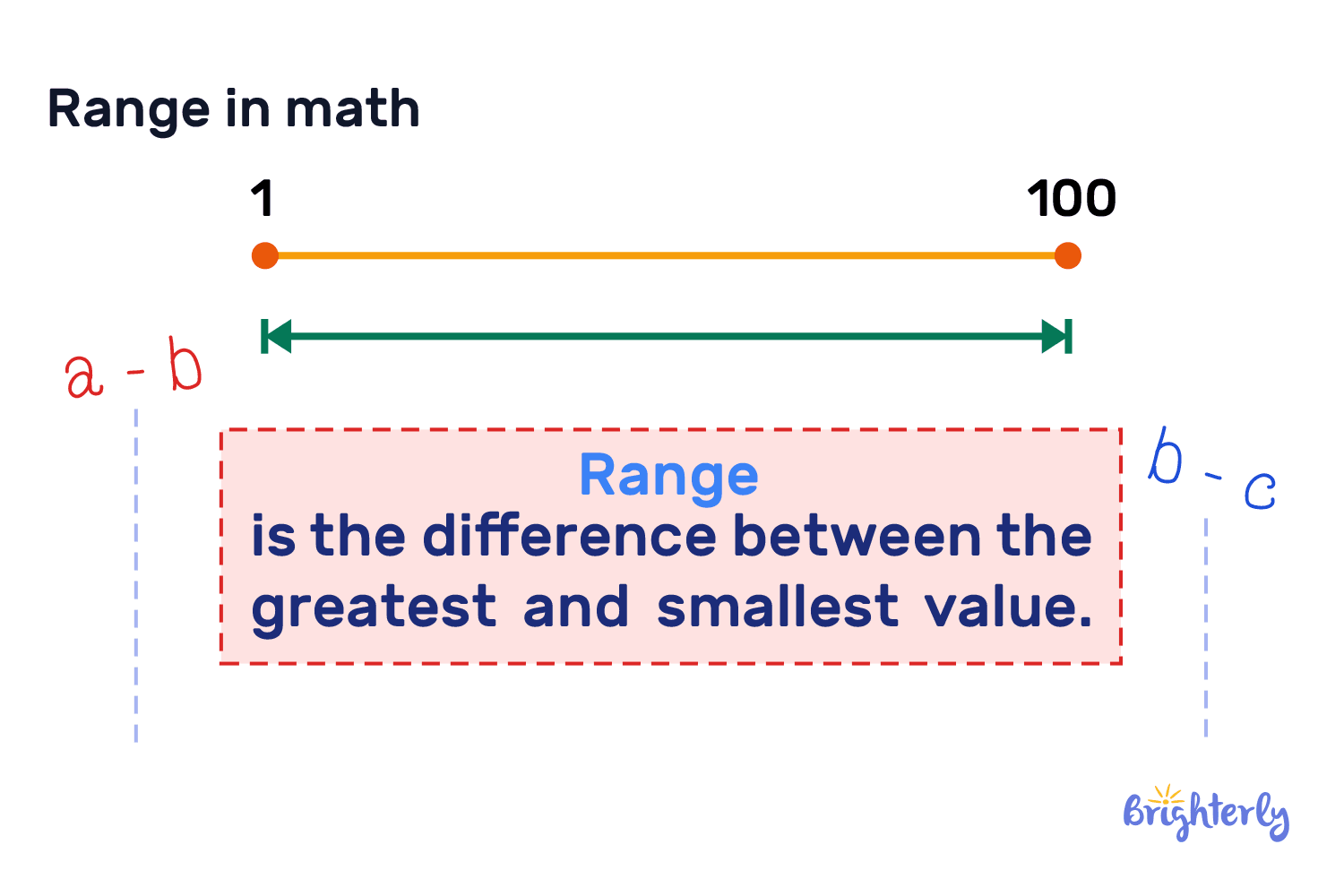
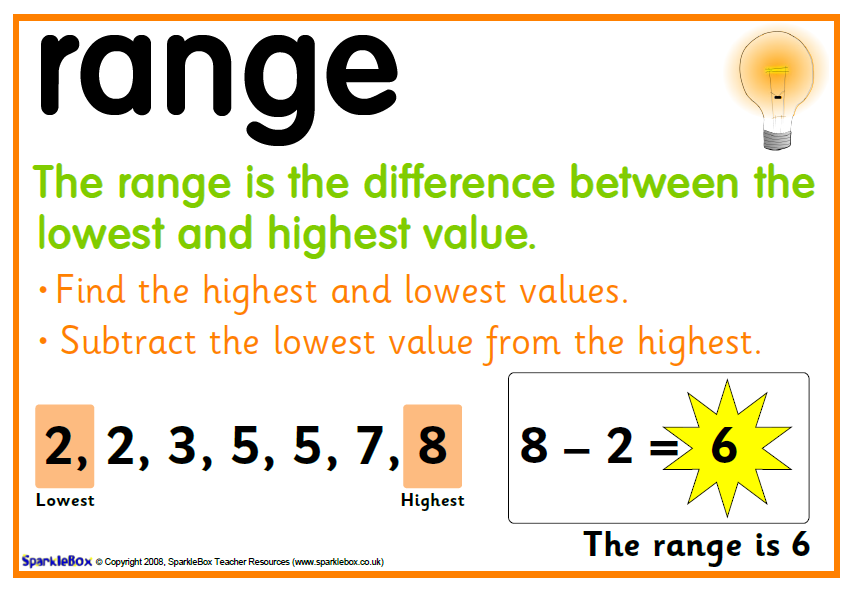
Alright, let’s start with the basics. In simple terms, the range in math is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a set of numbers. Think of it as the span or spread of data. For example, if you have a list of numbers like 5, 12, 3, and 20, the range would be 20 (the highest number) minus 3 (the lowest number), which equals 17. Easy peasy, right?
Now, why is the range important? Well, it gives us a quick snapshot of how spread out the data is. If the range is small, it means the numbers are close together. If it’s large, the numbers are more spread apart. This concept is super useful in fields like statistics, where analyzing data is key.
Here’s a quick breakdown of how to calculate the range:
- Identify the highest value in the data set.
- Identify the lowest value in the data set.
- Subtract the lowest value from the highest value.
Let’s take another example. If you have the numbers 10, 15, 25, and 30, the range would be 30 (highest) minus 10 (lowest), which equals 20. See? Not too complicated!
The Role of the Range in Statistics
In the world of statistics, the range plays a crucial role. It’s one of the measures of variability, meaning it helps us understand how much the data varies. Alongside other measures like mean, median, and mode, the range gives us a complete picture of the data set.
For instance, imagine you’re analyzing test scores in a classroom. The range would tell you how far apart the highest and lowest scores are. If the range is small, it means most students scored similarly. If it’s large, it indicates a wider variation in performance.
Read also:Whats The Difference Between Peanut Butter And Jam A Delicious Debate
Here’s a fun fact: The range is often used in real-life situations, like tracking stock prices or monitoring weather conditions. For example, if you’re looking at daily temperatures over a week, the range would show you the difference between the hottest and coldest days.
Why is the Range Important in Data Analysis?
Data analysis is all about making sense of numbers, and the range is a key player in this process. It helps identify outliers, which are numbers that are significantly higher or lower than the rest of the data. Outliers can skew results, so understanding the range helps us spot them and decide whether they should be included in our analysis.
Let’s say you’re analyzing monthly sales data for a business. If one month’s sales are way higher or lower than the others, it could be an outlier. The range would highlight this discrepancy, allowing you to investigate further.
Common Misconceptions About the Range
There are a few common misconceptions about the range that we need to clear up. First, some people think the range is the same as the average or mean. Not true! The range only measures the spread of data, while the mean calculates the average value.
Another misconception is that the range is always a large number. Actually, the range can be small or large depending on the data set. For example, the range of the numbers 1, 2, and 3 is just 2, which is pretty small.
Lastly, some folks assume the range is the only measure of variability. While it’s an important one, there are others like variance and standard deviation that provide even more detailed insights into data spread.
How to Avoid Misinterpreting the Range
One of the best ways to avoid misinterpreting the range is to always look at the full context of the data. For example, if you’re analyzing a small data set, the range might not give you the whole picture. In such cases, combining the range with other measures like the mean and median can provide a more accurate understanding.
Another tip is to visualize the data using tools like graphs or charts. This can help you see patterns and trends that numbers alone might not reveal. For instance, a bar graph can show you how the data is distributed and whether there are any outliers.
Applications of the Range in Real Life
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s talk about how the range is used in real life. As it turns out, this concept has a ton of practical applications. Here are a few examples:
- Finance: Investors use the range to analyze stock price fluctuations over time. It helps them identify trends and make informed decisions.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use the range to track temperature variations and predict weather patterns.
- Education: Teachers use the range to evaluate student performance and identify areas that need improvement.
- Healthcare: Doctors use the range to monitor vital signs like blood pressure and heart rate, ensuring they stay within normal limits.
These are just a few examples, but the possibilities are endless. The range is a versatile tool that can be applied to almost any field where data analysis is involved.
Real-Life Case Study: Using the Range in Business
Let’s take a closer look at how the range is used in the business world. Imagine you’re the owner of a small retail store. You want to analyze your monthly sales data to identify trends and make better decisions. By calculating the range of your sales, you can see how much your revenue varies from month to month.
For example, if your sales range from $5,000 to $15,000 per month, you know there’s a significant variation. This could prompt you to investigate further and find ways to stabilize your sales. Maybe you need to adjust your marketing strategy or offer promotions during slower months.
Advanced Concepts: Beyond the Basics of the Range
Once you’ve mastered the basics of the range, you can dive into more advanced concepts. For example, you can explore how the range relates to other statistical measures like variance and standard deviation. These concepts provide deeper insights into data spread and variability.
Variance measures how far each number in the data set is from the mean, while standard deviation is the square root of variance. Both of these measures are closely related to the range and can be used together to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data.
Another advanced concept is the interquartile range (IQR), which measures the spread of the middle 50% of the data. The IQR is often used in conjunction with the range to identify outliers and provide a more detailed analysis.
How to Calculate the Interquartile Range
Calculating the interquartile range involves a few steps:
- Arrange the data in ascending order.
- Find the median, which is the middle value of the data set.
- Split the data into two halves: the lower half and the upper half.
- Find the median of each half, which are called the first quartile (Q1) and the third quartile (Q3).
- Subtract Q1 from Q3 to get the interquartile range.
For example, if Q1 is 10 and Q3 is 30, the IQR would be 20. This tells you that the middle 50% of the data falls within a range of 20 units.
Tips and Tricks for Working with the Range
Now that you know the ins and outs of the range, here are a few tips to help you work with it more effectively:
- Use Technology: Tools like Excel, Google Sheets, or statistical software can make calculating the range a breeze. Just input your data and let the software do the math for you.
- Visualize the Data: Graphs and charts can help you see the data spread more clearly. Try using bar graphs, line graphs, or box plots to visualize the range.
- Combine with Other Measures: Always consider the range in conjunction with other statistical measures like mean, median, and mode for a more complete analysis.
These tips will not only make your life easier but also help you gain deeper insights into the data you’re working with.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using the Range
Even though the range is a simple concept, there are a few common mistakes to watch out for:
- Ignoring Outliers: Outliers can skew the range, so it’s important to identify and address them properly.
- Overreliance on the Range: While the range is useful, it shouldn’t be the only measure you rely on. Combine it with other statistical tools for a more accurate analysis.
- Misinterpreting the Range: Always consider the context of the data and avoid jumping to conclusions based solely on the range.
Conclusion: Mastering the Range in Math
In conclusion, the range in math is a powerful tool that helps us understand how data is spread out. Whether you’re analyzing test scores, tracking weather patterns, or evaluating business performance, the range provides valuable insights into data variability. By mastering this concept and combining it with other statistical measures, you can gain a deeper understanding of the numbers around you.
So, the next time someone asks you, “What is the range in math?” you’ll be able to confidently explain it and even impress them with your knowledge. Remember, math doesn’t have to be scary. With the right tools and mindset, anyone can become a data analysis pro.
Now, it’s your turn. Have you used the range in math before? What are some of your favorite tips and tricks for working with data? Leave a comment below and let’s keep the conversation going. And don’t forget to share this article with anyone who might find it helpful. Happy analyzing!
Daftar Isi
- Understanding the Basics: What Exactly is the Range in Math?
- The Role of the Range in Statistics
- Common Misconceptions About the Range
- Applications of the Range in Real Life
- Advanced Concepts: Beyond the Basics of the Range
- Tips and Tricks for Working with the Range
- Conclusion: Mastering the Range in Math